LEARN: PMS vs PMDD
PMS vs PMDD
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) are related conditions that occur before menstruation, but they differ in severity and impact:
PMS
- Affects up to 75% of menstruating women
- Characterized by mild to moderate physical and emotional symptoms
- Typically doesn't significantly disrupt daily life
- Symptoms may include bloating, tender breasts, mood swings, and fatigue
PMDD
- Affects 3-8% of menstruating women
- A more severe form of PMS, classified as a depressive disorder
- Causes significant disruption to daily life and relationships
- Symptoms include severe mood swings, depression, anxiety, and irritability
Key Differences
- Severity: PMDD symptoms are more intense and debilitating than PMS12.Emotional impact: PMDD has a more pronounced effect on mood and mental health.
- Diagnosis: PMDD is a recognized mental health condition in the DSM-5, while PMS is not.
- Duration: PMDD symptoms typically last longer, up to two weeks before menstruation2.
Managing PMS and PMDD Together
Managing these conditions together can be beneficial because:
- Overlapping symptoms: Many symptoms are similar, allowing for some shared management strategies.
- Holistic approach: Addressing both conditions promotes overall menstrual health.
- Continuity of care: It allows for better tracking and management of symptoms across the spectrum.
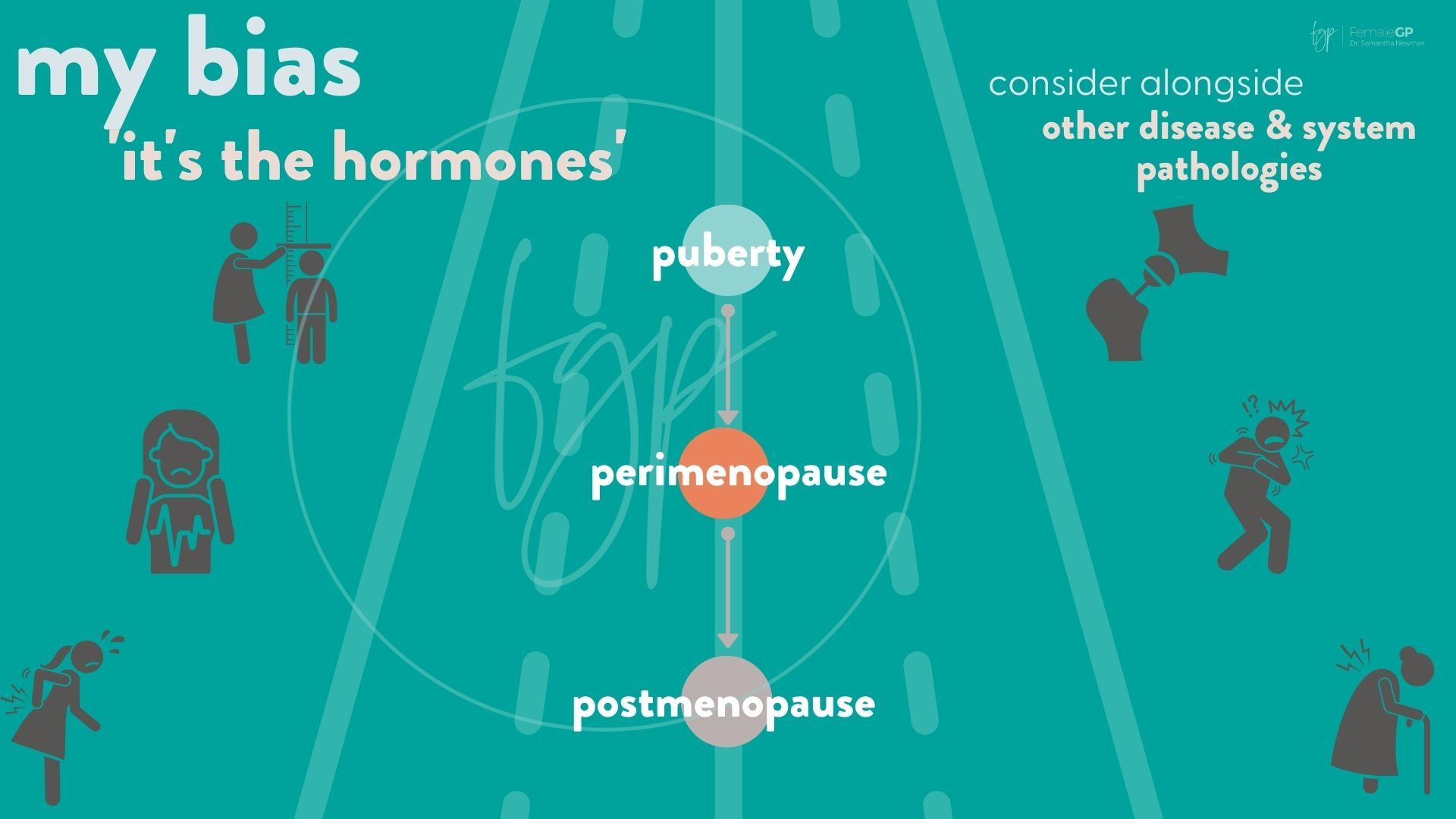
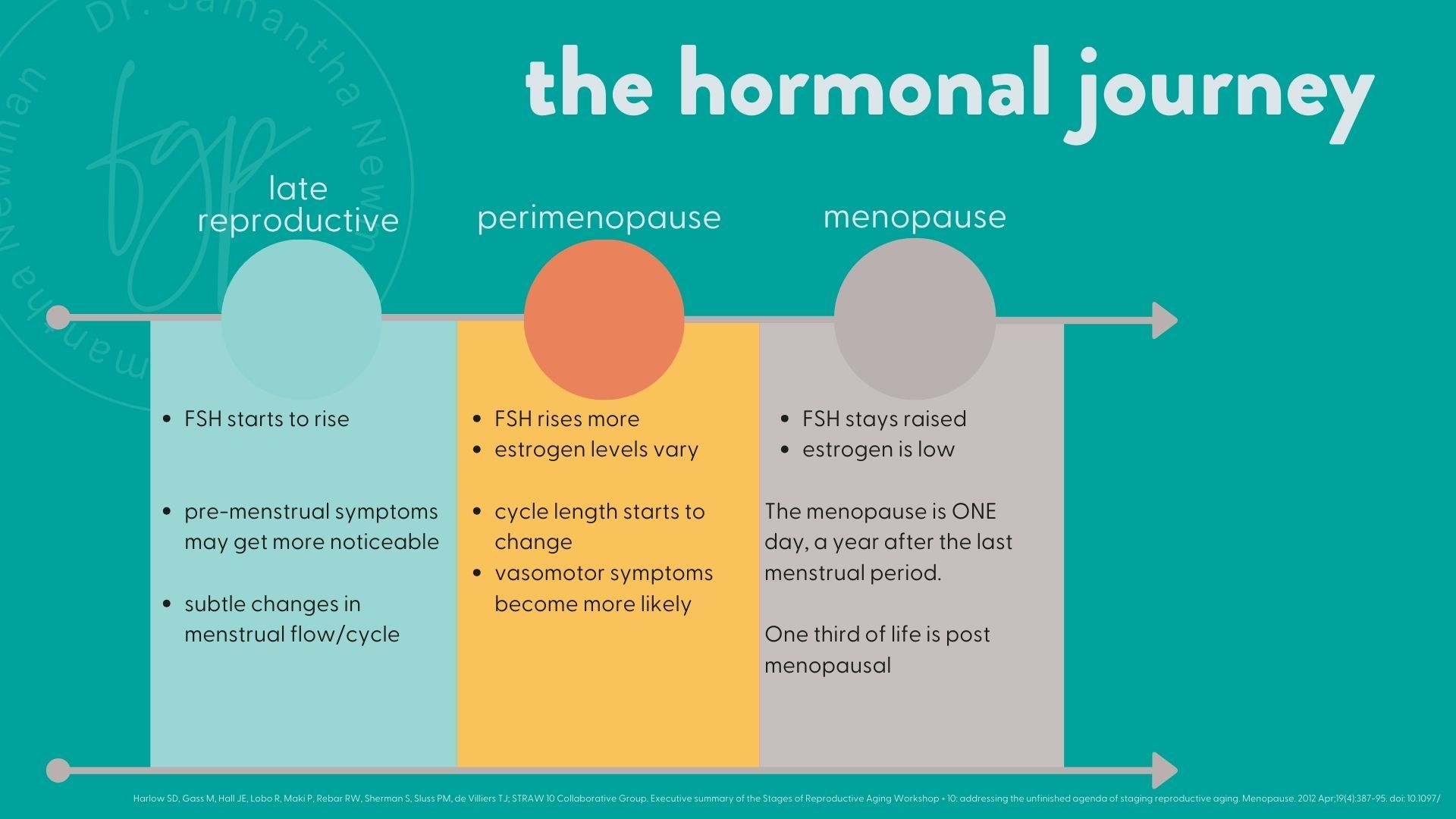
Lessons from Perimenopause Management
In my practice with midlife women and menopause I have noticed many patterns in perimenopause management and PMS/PMDD. It is generalising to say it is a continuum, but there are definitely parallels. Once again, a sweeping statement is that 'it's the same management'. I don't think it is specifically, but the principles are. This is why I manage all hormonal menstrual changes - because it is part of the journey and understand your own nuances.
Managing perimenopause alongside PMS and PMDD can provide valuable insights:
- Hormonal fluctuations: All three conditions involve hormonal changes, emphasizing the importance of hormone balance.
- Lifestyle factors: Similar lifestyle modifications (e.g., diet, exercise, stress management) can benefit all three conditions.
- Individualized treatment: Each woman's experience is unique, requiring personalized approaches.
- Long-term perspective: Understanding the continuum of reproductive health from menstruation to menopause aids in comprehensive care. For example if you have had PMDD then you are more likely to experience perimenopause/menopause depression. Therefore I would like to prepare you for this.
Treatment Approaches
- Lifestyle modifications: Exercise, healthy diet, stress reduction, and good sleep hygiene
- Medications: SSRIs for PMDD, hormonal birth control for both conditions or hormone replacement therapy. Some individuals also benefit from higher dose progesterone, but for others this is a disaster. Professor Studd, in the 1980's also reported a benefit in testosterone.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy: Helpful for managing emotional symptoms in both PMS and PMDD
- Tracking symptoms: Essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment of both conditions
By managing PMS and PMDD together and incorporating lessons from perimenopause management, healthcare providers can offer more comprehensive, effective care throughout a woman's reproductive life.