INVESTIGATION: USS
Pelvic Ultrasound Scans
INVESTIGATION: USS
Pelvic Ultrasound Scans
A pelvic ultrasound (USS) is a non-invasive imaging test that helps visualize the organs and structures within the pelvis. It's often used to examine the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and bladder in wome n.
There are two main types of pelvic ultrasound. The transabdominal ultrasound involves moving a handheld device called a transducer across the lower abdomen, using gel to help transmit sound waves and create real-time images of the pelvic organs. The transvaginal ultrasound provides a closer, more detailed view by gently inserting a transducer into the vagina, resulting in higher-resolution images of the uterus and ovaries.
Pelvic ultrasounds are commonly used to investigate conditions like ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and to monitor pregnancy or assess unexplained pelvic pain or abnormal bleeding. The procedure is painless and typically lasts 15 to 30 minutes.
A pelvic ultrasound is often recommended for abnormal menstrual bleeding because it helps identify potential underlying causes by providing clear images of the pelvic organs. It allows healthcare providers to evaluate the uterus, endometrium (lining of the uterus), ovaries, and cervix for any abnormalities contributing to irregular or heavy bleeding.
Some reasons for conducting a pelvic ultrasound to investigate abnormal menstrual bleeding include the presence of fibroids, which are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy or prolonged bleeding. Endometrial polyps are growths in the lining of the uterus that may lead to irregular or heavy bleeding. Measuring endometrial thickness can help assess abnormalities, especially in peri- and post-menopausal women. Ovarian cysts can also cause irregular bleeding or menstrual cycle disturbances. Adenomyosis is a condition where the inner lining of the uterus breaks through the muscle wall, resulting in painful and heavy periods. Endometrial hyperplasia is an abnormal thickening of the uterine lining, which can be a precursor to cancer in some cases. Additionally, uterine or cervical abnormalities, such as malformations or structural issues, may contribute to irregular bleeding.
These tips can help you prepare for a pelvic ultrasound (USS)
Hydration: Drink plenty of water before the exam to ensure your bladder is full, as this can help provide clearer images during a transabdominal ultrasound. Aim to drink about 1 litre an hour before the appointment and avoid urinating until after the scan. Having a bigger bladder helps get a better picture!
Vaginal bleeding/your menstrual cycle: If you are having menstrual cycles then the optimum time to assess the endometrial lining is after your period, this is when the lining is it's thinnest. Generally, if you are post menopausal and not having periods then the scan can be done at any time. But, I always recommend my patients do not worry if you are menstruating, the scan can still be done. From a medical perspective it is important not to keep putting off the scan because that can delay you receiving timely healthcare. However, if delaying the scan for a few days would be more comfortable for you please do ask the Scan Company, as they are usually really happy to support you with this
Foods: Occasionally the bowel can be full of gas and that stops the sonographer getting good pictures of the pelvic organs. If you get particularly gassy or bloated from specific foods you may want to avoid them the day before, just in case!
Medications: Continue taking your regular medications unless your provider advises otherwise.
Wear Comfortable Clothing: Choose loose-fitting clothing that can be easily adjusted or removed for the exam. You may need to change into a gown.
Discuss Concerns: If you have any questions or concerns about the procedure, don't hesitate to discuss them with your healthcare provider beforehand or talk to the sonographer
The Scan
This is a photo of a sonographer (person who does the scanning) with a probe (the camera) on a person. They will be looking at what is going on inside the body. They will likely use some jelly on your tummy to help the camera work. It can feel cold! The sonographers usually stop the gel getting on your clothes by protecting them with papers towels.
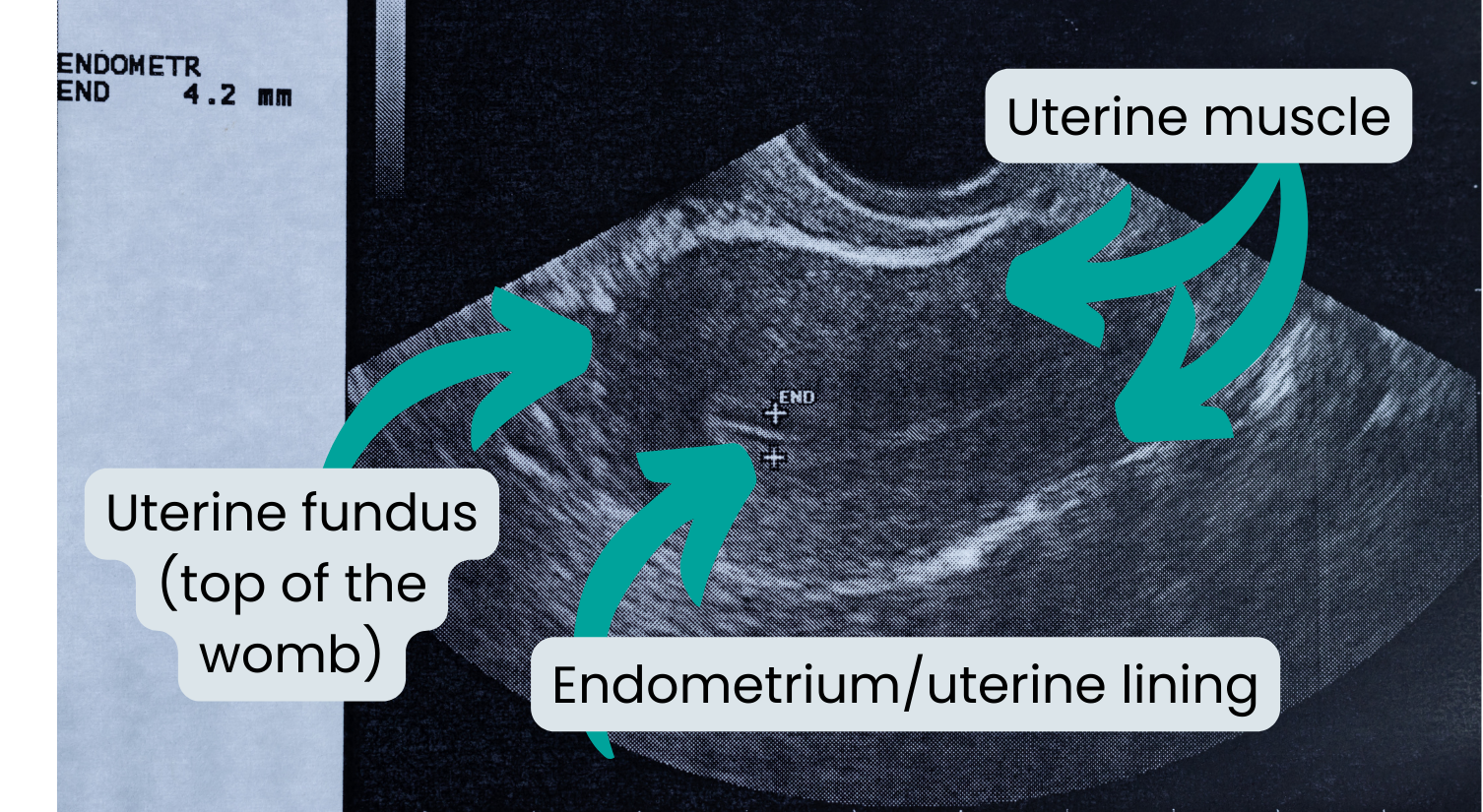
The uterus
The uterus (wharetangata, or womb) can be seen in this picture subtly outlined by a brighter colour. The uterus is usually about 6-11 cm in length so the pictures are often enlarged. For abnormal menstrual/vaginal bleeding the sonographer needs to look at the endometrium and measure it. As thicker endometrial linings/womb linings can be a sign that we need to look a bit further
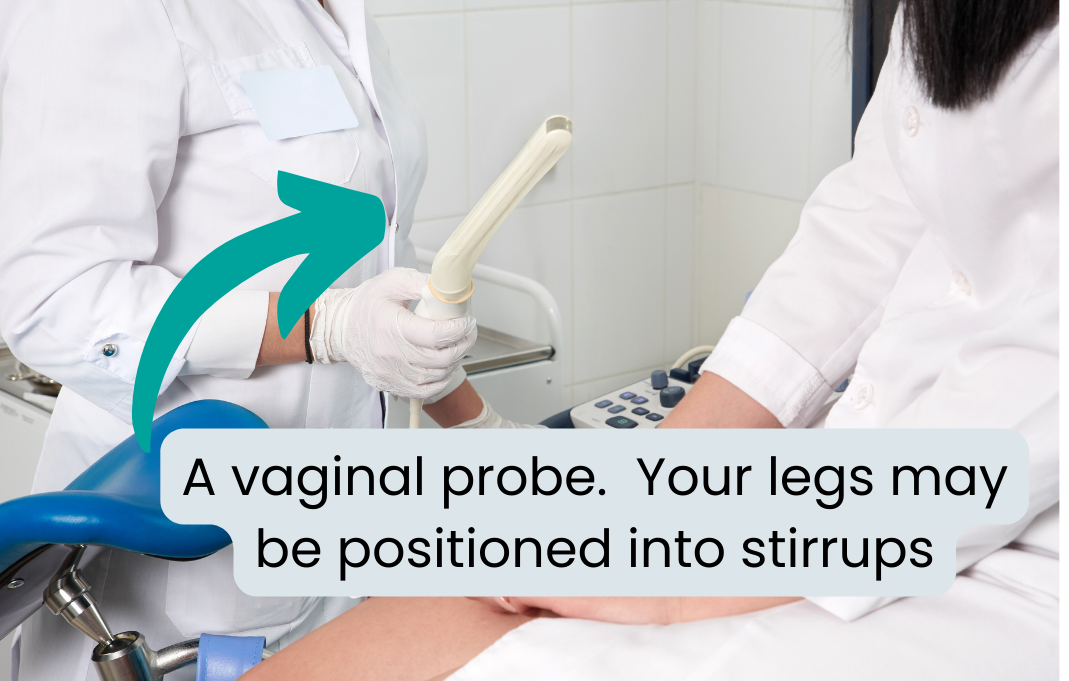
Vaginal examinations
For many health questions a vaginal or pelvic ultrasound is needed. This can be a worry for some women, however the sonographer is very experienced and trained in this. It can be a bit uncomfortable (often weird!, but it shouldn't be painful. You will be able to ask them to stop at any time. An internal scan is recommended if you have/have had endometriosis, pelvic surgery (including cesarean sections), a womb that tilts back (retroverted uterus), and in women with a highter BMI.